Annotating nextflow processed data
2025-10-24
Source:vignettes/annotate-nf-processed-data.Rmd
annotate-nf-processed-data.RmdOverview
This vignette shows how to automatically generate metadata manifests and provenance information for data processed by nextflow workflows (nf-rnaseq and nf-sarek). These manifests can be validated and submitted to annotate files in Synapse or create Synapse Datasets.
What you’ll learn
- How to extract workflow metadata automatically from
pipeline_info - How to generate annotation manifests for processed outputs
- How to add provenance linking outputs to inputs
- How to create Synapse Datasets from manifests
Prerequisites
- READ access to processed workflow outputs in Synapse
- DOWNLOAD access to the input samplesheet (or a local copy)
- EDIT access to apply annotations (for final submission step)
- A Synapse fileview that includes the workflow
output files
-
Important: The fileview must have the
pathcolumn enabled (this is required for output discovery)
-
Important: The fileview must have the
Setup
Load the package and log in with your Synapse authentication token:
library(nfportalutils)
library(data.table)
syn_login() # Requires SYNAPSE_AUTH_TOKEN environment variableQuick Start: nf-rnaseq
Here’s a complete example annotating RNA-seq outputs with a single function call:
# Simplest usage - everything auto-detected from standard workflow
result <- annotate_nf_workflow(
publish_dir = "syn66351496", # Top-level output directory (contains pipeline_info and star_salmon)
fileview = "syn51301431", # Fileview scoping the output files, *must* contain `path`
workflow = "nf-rnaseq" # Workflow type
)
# Inspect results
names(result$manifests) # Available output types
head(result$manifests$`STAR and Salmon`) # View manifest
result$workflow_info # Workflow name and versionThat’s it! The function automatically:
- Finds the samplesheet at
pipeline_info/samplesheet.valid.csv - Extracts workflow version from
pipeline_info/software_versions.yml - Parses the input samplesheet
- Discovers all available output types (which can depend on how workflow was run and how files were indexed back to Synapse)
- Generates properly annotated manifests for each output type
Optional/advanced parameters are available for: - Custom samplesheet location (e.g., manually corrected version) - Non-standard output folder organization - Selecting specific output types - Custom sample name parsing
How it works
Understanding nextflow outputs
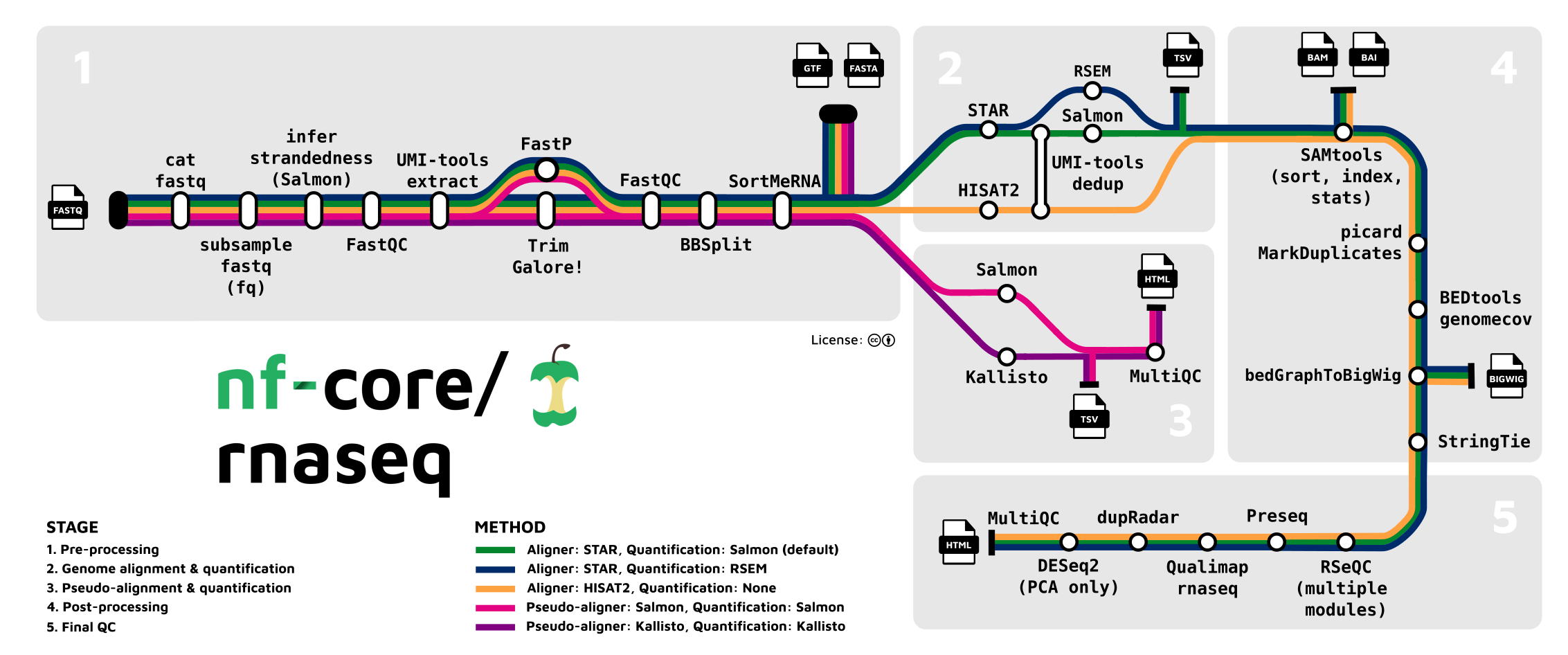
Nextflow workflows generate different types of outputs at various steps (see figure above). At certain steps, we have products that can be packaged into “level 2, 3, or 4” datasets suitable for downstream analysis or sharing. For example:
-
.bam/.baifiles from SAMtools represent level 2 aligned reads -
.sffiles from STAR and Salmon represent level 3 quantified expression data -
.vcffiles from variant callers represent level 3 variant calls
The goal is to point to a workflow output folder and automatically get back annotation manifests for all useful dataset products. The utilities automatically identify which output types are present and generate appropriate metadata for each.
The annotation workflow
The annotate_nf_workflow() function automatically:
-
Extracts workflow version from
pipeline_info/software_versions.ymlusingnf_workflow_version() - Parses the input samplesheet to identify which raw files were processed
- Discovers processed outputs by querying the fileview for specific output types (e.g., BAM files, quantification files)
- Links inputs to outputs by matching sample identifiers from filenames and folder structure
-
Transfers metadata from input files to output files
(e.g.,
individualID,assay, specimen attributes) -
Applies workflow-specific annotations based on
output type (e.g.,
dataType,fileFormat,expressionUnit)
The function returns a list with:
-
manifests: Named list of annotation manifests for each output type -
sample_io: Input-output mappings for provenance tracking -
workflow_info: Workflow name and version extracted fromsoftware_versions.yml
Step-by-step workflow (advanced)
If you need more control over individual steps, you can use the underlying functions directly:
# 1. Extract workflow version
wf_info <- nf_workflow_version(syn_out)
wf_link <- sprintf("https://nf-co.re/rnaseq/%s/output#star-and-salmon", wf_info$version)
# 2. Parse input samplesheet
input <- map_sample_input_ss(samplesheet)
# 3. Map outputs
output <- map_sample_output_rnaseq(syn_out, fileview)
# 4. Generate manifests
meta <- processed_meta(input, output, workflow_link = wf_link)Understanding samplesheets
Samplesheets are CSV files used by nextflow workflows to specify
input files. They’re typically found in the pipeline_info
directory after a workflow completes.
Requirements: The samplesheet must contain valid Synapse IDs in the fastq columns. The parser handles various formats:
✔ Valid formats:
#> sample fastq_1 fastq_2 strandedness
#> 1 JH-2-019-DB5EH-C461C syn15261791 syn15261900 auto
#> 2 JH-2-007-B14BB-AG2A6 syn15261974 syn15262033 auto#> sample fastq1 fastq2
#> 1 JHU002-043 syn://syn22091879 NA
#> 2 JHU023-044 syn://syn22091973 NA✖ Invalid format:
#> sample fastq_1
#> 1 patient10tumor1_T1 s3://some-tower-bucket/syn40134517/x6/SL106309_1.fastq.gz
#> fastq_2
#> 1 s3://some-tower-bucket/syn40134517/syn7989839/SL106309_2.fastq.gzNote: If you encounter parsing errors, verify that all fastq paths contain valid Synapse IDs. You may need to manually correct the samplesheet.
Available output types
nf-rnaseq outputs:
-
STAR and Salmon: Gene quantification files (.sf) with TPM values- Annotations:
dataType,fileFormat,expressionUnit,workflowLink - QC metrics: None automatically added
- Annotations:
-
featureCounts: Count matrices (.txt)- Annotations:
dataType,fileFormat,expressionUnit,workflowLink - QC metrics: None automatically added
- Annotations:
-
SAMtools: Aligned reads (.bam/.bai)- Annotations:
dataType,fileFormat,genomicReference,workflowLink -
QC metrics automatically added (from MultiQC
SAMtools stats):
averageInsertSizeaverageReadLengthaverageBaseQualitypairsOnDifferentChrreadsDuplicatedPercentreadsMappedPercenttotalReads
- Annotations:
nf-sarek outputs:
-
DeepVariant,Strelka2,Mutect2,FreeBayes: Variant calls (.vcf.gz/.tbi)- Annotations:
dataType,fileFormat,workflowLink - QC metrics: None automatically added
- Annotations:
-
CNVkit: Copy number analysis files- Annotations:
dataType,fileFormat,workflowLink - QC metrics: None automatically added
- Annotations:
Use ?map_sample_output_rnaseq or
?map_sample_output_sarek for details.
Note: Actual output availability depends on workflow parameters and which files were indexed to Synapse. QC metrics for aligned reads follow the GDC AlignedReads model.
# Check which outputs are available
output <- map_sample_output_rnaseq(syn_out, fileview)
names(output)Submitting annotations
1. Review and adjust manifests
# Inspect manifest
manifest_salmon <- result$manifests$`STAR and Salmon`
head(manifest_salmon)
# Adjust annotations if needed (manifests are just data.tables)
# For example, if your workflow used a different genome reference:
manifest_bam <- result$manifests$SAMtools
manifest_bam$genomicReference <- "GRCh37" # Change from default GRCh38Note: The genomicReference for aligned
reads defaults to GRCh38. If your workflow used a different
reference genome (e.g., GRCh37, mm10), simply update the manifest table
before submission.
2. Validate manifest (recommended)
We expect the result to valid, but it never hurts to check in case the latest data model specifications has changes that need code updates.
# To validate, you must write out to a file first
fwrite(manifest_salmon, "manifest.csv")
# This may take a couple of minutes, depending on size
manifest_validate(data_type = "ProcessedExpressionTemplate", file = "manifest.csv")3. Submit annotations to Synapse
annotate_with_manifest(manifest_salmon)4. Add provenance
Link processed outputs to their raw input files:
sample_io <- result$sample_io
# Extract workflow link from the result
wf_link <- sprintf(
"https://nf-co.re/rnaseq/%s/output#star-and-salmon",
result$workflow_info$version
)
add_activity_batch(
entities = sample_io$output_id,
act_name = sample_io$workflow,
act_executed = wf_link,
used_inputs = sample_io$input_id
)Provenance establishes the computational lineage: raw data → workflow → processed data.
5. Create Synapse Dataset (recommended)
Package the annotated files into a Synapse Dataset object:
dataset_salmon <- new_dataset(
name = "STAR Salmon Gene Expression Quantification",
parent = "syn12345678", # Your project id
items = manifest_salmon$entityId,
dry_run = FALSE
)nf-sarek workflow
The process is identical to nf-rnaseq, just specify
workflow = "nf-sarek":
# Generate manifests for sarek workflow
result <- annotate_nf_workflow(
syn_out = "syn27650634",
fileview = "syn13363852",
workflow = "nf-sarek",
samplesheet = "syn38793905"
)
# View available manifests
names(result$manifests)
head(result$manifests$Strelka2)Sarek provenance with caller-specific links
For variant calling, you can provide caller-specific documentation links:
# Create caller-specific workflow links using extracted version
wf_links <- c(
FreeBayes = sprintf("https://nf-co.re/sarek/%s/output#freebayes", result$workflow_info$version),
Mutect2 = sprintf("https://nf-co.re/sarek/%s/output#gatk-mutect2", result$workflow_info$version),
Strelka2 = sprintf("https://nf-co.re/sarek/%s/output#strelka2", result$workflow_info$version)
)
sample_io <- result$sample_io
add_activity_batch(
entities = sample_io$output_id,
act_name = sample_io$workflow,
act_executed = wf_links[sample_io$workflow],
used_inputs = sample_io$input_id
)Troubleshooting
Common issues:
- Missing or incorrect annotations on outputs: Check that input files have complete, correct annotations. Outputs inherit metadata from inputs.
-
Parsing errors: Verify samplesheet contains valid
Synapse IDs. Use
map_sample_input_ss()on a local corrected copy if needed. - Missing outputs: Ensure files are indexed to Synapse and included in the fileview. Check workflow parameters to confirm outputs were generated.
- Non-standard organization: The utils expect standard nf-core output structure. Custom workflows may require manual adjustments.
Best practices:
- Always use
dry_run = TRUEwhen testing annotation or dataset creation functions - Validate manifests with schematic before bulk submission
- Keep workflow outputs in standard nf-core directory structure
- Maintain complete annotations on raw input files
Advanced usage
Using local samplesheets
result <- annotate_nf_workflow(
syn_out = "syn51476810",
fileview = "syn11601481",
workflow = "nf-rnaseq",
samplesheet = "~/work/corrected_samplesheet.csv" # Local path
)Custom sample parsing
# Custom function to parse sample names (e.g., remove technical replicate suffix)
result <- annotate_nf_workflow(
syn_out = "syn51476810",
fileview = "syn11601481",
workflow = "nf-rnaseq",
samplesheet = "syn51408030",
parse_fun = function(x) gsub("_rep[0-9]$", "", x)
)Selecting specific outputs
# Only process STAR and Salmon outputs (skip BAM files and featureCounts)
result <- annotate_nf_workflow(
syn_out = "syn51476810",
fileview = "syn11601481",
workflow = "nf-rnaseq",
samplesheet = "syn51408030",
output_types = "STAR and Salmon"
)Auto-detecting samplesheet
For newer workflows, the samplesheet can be auto-detected:
# Omit samplesheet parameter - will search in pipeline_info
result <- annotate_nf_workflow(
syn_out = "syn51476810",
fileview = "syn11601481",
workflow = "nf-rnaseq"
)